Every day, people lose between 50 and 100 hairs. This is a natural part of how hair grows. But, many mix up ‘hair shedding’ and ‘hair loss.’ This mix-up can cause worry about the health of your hair. While losing some hair is normal, too much shedding can point to problems. Stress or hormonal changes might be to blame, and you might need to look into it.
It’s important to know about hair health if you care about your hair. Hair shedding and hair loss are not the same. Shedding is usually no big deal and stops on its own. But, hair loss could be permanent and might need a doctor’s help. Knowing the difference helps you take care of your hair better. If necessary, you can get help from a professional. For more on this topic, check out this informative article.
Key Takeaways
- The average individual sheds between 50 and 100 hairs each day, which is considered normal.
- Excessive hair shedding, often due to stress or dietary factors, can be a sign of telogen effluvium.
- The distinction between hair shedding and hair loss is significant for appropriate treatment approaches.
- Early treatment for hair loss can often reverse the condition effectively.
- Prose shampoo and conditioner can significantly reduce hair breakage and improve overall hair health.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to managing hair shedding and preventing permanent loss.
Understanding Hair Shedding
Hair shedding is natural, part of our body’s hair growth cycle. Every day, people lose around 50 to 100 hairs. Knowing about this helps tell the difference between normal shedding and serious hair loss.
What is Hair Shedding?
Hair shedding happens during the normal hair cycle. This cycle has four phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), telogen (resting), and exogen (shedding). Shedding is normal and changes from person to person. During the growth phase, about 85% of hair is growing. The rest, 15%, is getting ready to shed.
The Hair Growth Cycle Explained
The hair growth cycle has few phases that affect hair’s health and length. Here are the phases explained:
| Phase | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Anagen | Active growth phase where hair follicles produce new hair. | 2 to 6 years |
| Catagen | Transition phase where hair growth slows and hair follicles shrink. | 2 to 3 weeks |
| Telogen | Resting phase before hair shedding occurs; hair is not actively growing. | 3 to 4 months |
| Exogen | Shedding phase where old hair falls out, making way for new growth. | 2 to 5 months |
Normal Amounts of Hair Shedding
It’s normal to shed 50 to 100 hairs daily. But losing more than 150 hairs a day could mean there’s a problem. Stress and poor diet can cause hair loss, among other things. So, living a healthy life is key for good hair health. If you notice a lot of hair falling out, seeing a dermatologist is a good idea. They can help find out what’s going on and how to fix it.
Excessive Hair Shedding: When is it a Concern?
It’s normal to shed hair every day as part of our hair’s growth cycle. Yet, when shedding becomes excessive, it can be worrying. Recognizing the signs and understanding what causes heavy shedding is key to tackling the issue.
Signs of Excessive Shedding
If you’re losing more hair than usual, you might notice certain signs. These include finding:
- Clumps of hair on your pillows or in the shower drain
- More hair in your brush after using it
- Thinning areas on your scalp
- That your hair seems weaker or thinner
Keeping an eye on these signs can help you decide if you need to see a doctor.
Common Causes of Excessive Hair Shedding
Many things can cause lots of hair to fall out. Knowing these reasons can help you figure out what to do next:
- Stress: Being under a lot of stress can cause hair to stop growing and shed.
- Hormonal Changes: Changes from childbirth or birth control can make your hair fall out more.
- Telogen Effluvium: This condition, often triggered by trauma or big health changes, leads to more shedding.
- Medical Conditions: Issues like thyroid problems or autoimmune diseases can cause lots of shedding.

Hair Loss: An Overview
Understanding hair loss, also called alopecia, is key to recognizing its types and impact. Hair loss is not just normal hair shedding. Normal shedding means losing 50 to 100 strands daily. But, hair loss is a more constant issue. It’s important to know the type of hair loss to find the right treatment and manage it well.
Defining Hair Loss (Alopecia)
Alopecia means different conditions that cause noticeable hair loss. It might show as thinning hair or bald spots on the scalp. Many things can lead to it, like changes in hormones, not getting the right nutrients, and genetic factors. Sometimes, too much hairstyling or health problems can make it worse.
Types of Hair Loss: Male and Female Patterns
It’s important to know the difference between male and female pattern baldness. Male pattern baldness affects about 30-50% of men. It usually starts at the hairline or the crown. Female pattern baldness is also common, affecting around 30% of middle-aged women. But for women, thinning happens all over the scalp, not in patches.
| Type of Alopecia | Demographics | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Male Pattern Baldness | Affects 30-50% of men | Recedes at hairline and crown, often a progressive condition |
| Female Pattern Baldness | Affects approx. 30% of middle-aged women | General thinning across the scalp; less pronounced than male pattern |
| Alopecia Areata | Affects both genders | Patchy hair loss; usually linked to autoimmune issues |
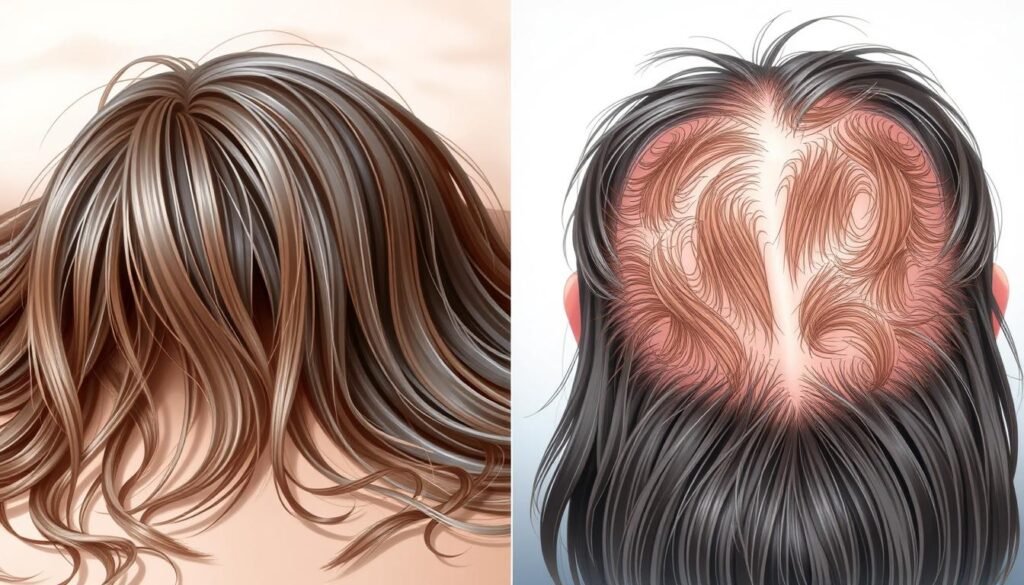
What Causes Hair Loss?
We need to understand what leads to hair loss to fight it. Many things can cause it, like genetic factors, hormone changes, medical issues, and getting older. This section talks about the main reasons for hair loss. This includes genes and hormones, as well as other medical problems.
Genetic Factors and Hormonal Influences
Genes play a big role in hair loss, especially with androgenetic alopecia. This condition affects many and shows up as thinning hair or baldness in both sexes. Hormones also have a big impact, especially during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. For example, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can make hair thin because of hormone problems. Understanding these can help people find the right way to deal with or avoid hair loss.
Medical Conditions and Other Contributing Factors
Hair loss can also come from health problems. Diseases like alopecia areata make hair fall out in patches. Problems with your thyroid can make your hair thin. Not getting enough vitamins, like biotin or iron, can make your hair fall out more. Stress can make a lot of hair fall out quickly, but it might grow back if the stress goes away. Tight hairstyles or strong hair treatments can also lead to hair loss.
| Factors | Examples | Effects on Hair |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Androgenetic alopecia | Baldness patterns in men and women |
| Hormonal Influences | PCOS, Menopause | Thinning hair, hair loss |
| Medical Conditions | Alopecia areata, Thyroid diseases | Patchy hair loss, thinning hair |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Iron, Biotin, Zinc | Significant shedding |
| Stress Factors | Childbirth, Illness | Telogen effluvium, temporary shedding |

Hair Shedding vs Hair Loss: Key Differences
Knowing how hair shedding differs from hair loss is key to managing them. Each condition has unique traits that affect how we treat them. Temporary hair loss can come from many places, while understanding hair shedding patterns can help us see our hair’s health.
Temporary vs Permanent Loss
Stress, sickness, or hormonal shifts can cause temporary hair loss. This usually means more hair falls out, but it grows back in six months to a year. But, some hair loss is forever, like when it’s due to genes or health issues. Knowing if your hair loss is temporary or permanent is vital. It can guide how you deal with it.
Patterns of Shedding and Loss
Looking at how your hair sheds can tell you a lot about its health. Normally, we lose 50 to 100 hairs a day. But losing more could signal a problem. Female pattern hair loss shows up as thin spots or bald places, unlike usual shedding. Knowing these signs can help find the right treatment.
Impact on Scalp and Hair Health
Hair shedding and loss both change our scalp and hair health, but differently. Temporary loss usually just makes hair thinner in spots, not bald. Conditions causing hair loss might need strong treatments. By understanding the differences between hair shedding and loss, you can act to keep your scalp and hair healthy.
Recognizing Signs of Hair Shedding vs Hair Loss
Understanding the difference between hair shedding and hair loss is key. It’s important for good hair health. Keeping an eye on how your hair changes can show if there’s a problem. If you notice something different, it’s wise to get help from a professional.
Identifying Symptoms of Hair Shedding
Normally, we lose 50 to 100 hairs a day. You might see hairs on your brush or in the shower. This shedding is part of the hair’s natural cycle and usually isn’t worrying. But, if you start shedding more than usual because of stress or diet changes, you might have telogen effluvium. This means you’re losing more hair for a few months, but it can get better.
Understanding Signs of Hair Loss
Hair loss shows up as clear patterns or bald spots. It happens when hair drops out but doesn’t grow back properly, which thins the hair out. Many things can cause hair loss, like genes, hormones, or health problems. If your scalp feels sore, looks red, or has sores, these could be signs that something serious is happening. Seeing an expert can help you find the right way to deal with it. They might suggest changing your routine or trying new treatments. More advice on this topic is available in this resource.
Treating Hair Shedding and Hair Loss
Combating hair shedding and loss involves a mix of methods. This is due to the different underlying causes. Identifying the right strategies can lead to healthier hair. Whether it’s changing your lifestyle or seeking medical help, many solutions can address hair shedding and loss effectively.
Effective Remedies for Hair Shedding
Natural remedies play a big role in controlling hair shedding. Eating a diet full of vitamins and minerals keeps hair healthy. Include nutrients like biotin, zinc, and omega-3s to strengthen hair and lessen shedding. Drinking enough water is also key to healthy hair.
Handling your hair gently can reduce loss. Techniques include:
- Using a wide-tooth comb for wet hair
- Avoiding tight hairstyles that pull at the roots
- Doing regular scalp massages to boost blood flow
You can find more details on hair shedding at this site.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss
There are many approaches to treat hair loss. Minoxidil, an over-the-counter drug, can encourage hair growth for some. Furthermore, finasteride, prescribed by doctors, battles androgenetic alopecia effectively.
Hair transplant surgery and laser therapy are more aggressive treatments. They work for those with serious hair loss. Laser therapy uses light to stimulate hair follicles, leading to growth.
Consulting a specialist is key for a tailored plan. A dermatologist or trichologist can pinpoint the most effective strategies. They might combine treatments and lifestyle adjustments for the best outcome.
Preventative Measures for Healthy Hair
Keeping your hair vibrant and healthy involves focusing on its care before problems start. Starting with a healthy hair lifestyle is key. It helps build strong, durable hair. We will explore how diet and gentle handling can keep your hair in top shape, preventing hair loss and damage.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet and Healthy Lifestyle
For gorgeous hair, eat a balanced diet full of needed nutrients. Vitamins, minerals, and proteins are vital for hair growth. Eat foods with omega-3, protein, iron, and vitamins A, C, and E. Drinking lots of water keeps your hair hydrated.
- Include nuts and seeds for omega-3 fatty acids.
- Consume leafy greens for vital vitamins and minerals.
- Opt for lean proteins such as chicken or fish to promote hair strength.
- Incorporate fruits rich in antioxidants to combat hair damage.
Gentle Hair Care Practices to Avoid Damage
Having a good diet and caring for your hair properly is essential. Avoid too much heat from hair tools and harsh chemicals to prevent damage. Get your hair trimmed regularly to avoid split ends. Less brushing can also mean less breakage, keeping your hair strong.
| Hair Care Practice | Benefits | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Limit Heat Styling | Reduces damage and splits | Use heat protectants |
| Gentle Cleansing | Maintains scalp health | Choose sulfate-free shampoos |
| Regular Trims | Prevents split ends | Cut every 6-8 weeks |
| Hydration | Supports hair elasticity | Drink plenty of water |
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between hair shedding and loss is key for good hair health. While it’s normal to lose some hair, too much shedding could mean problems. It’s important to understand what’s happening so you can handle it well.
Hair can shed a lot because of stress or it might not grow back due to genetics. It helps to know about this. Most times, shedding stops in six to nine months. But, hair loss might need extra steps to deal with. Getting help from experts and living healthy are crucial steps.
Staying informed about hair health leads to better care. It helps to catch problems early, making it easier to keep hair strong. By focusing on early care, you can lessen the effects of shedding or hair loss. This means your hair stays healthier in the long run.